Considerations for Basket Trial Design under Multisource Exchangeability Assumptions
Michael Kane, Yale University
Alex Kaizer, University of Colorado, Denver
Nan Chen, MD Anderson
Brian Hobbs, The Cleveland Clinic
Goals of this talk
Describe the use of multi-source exchangeability models in early Phase II basket trials using Vemurafenib as an example
Provide simulation results illustrating "power borrowing" among baskets and explore its implications in the study
Propose alternate basket constructions that are not based on indication
Vemurafenib
Causes programmed cell death in patients with V600E mutation
| Indication | Approval Date | Governing Body |
|---|---|---|
| Melanoma | August 17 2011 | FDA |
| Melanoma | Feb. 15 2012 | Health Canada |
| Melanoma | Feb. 20 2012 | European Commission |
| Erdheim-Chester Disease | November 6 2017 | FDA |
Approvals
Vemurafenib Label Expansion
Enrollment period April 11 2012 -- June 10 2014.
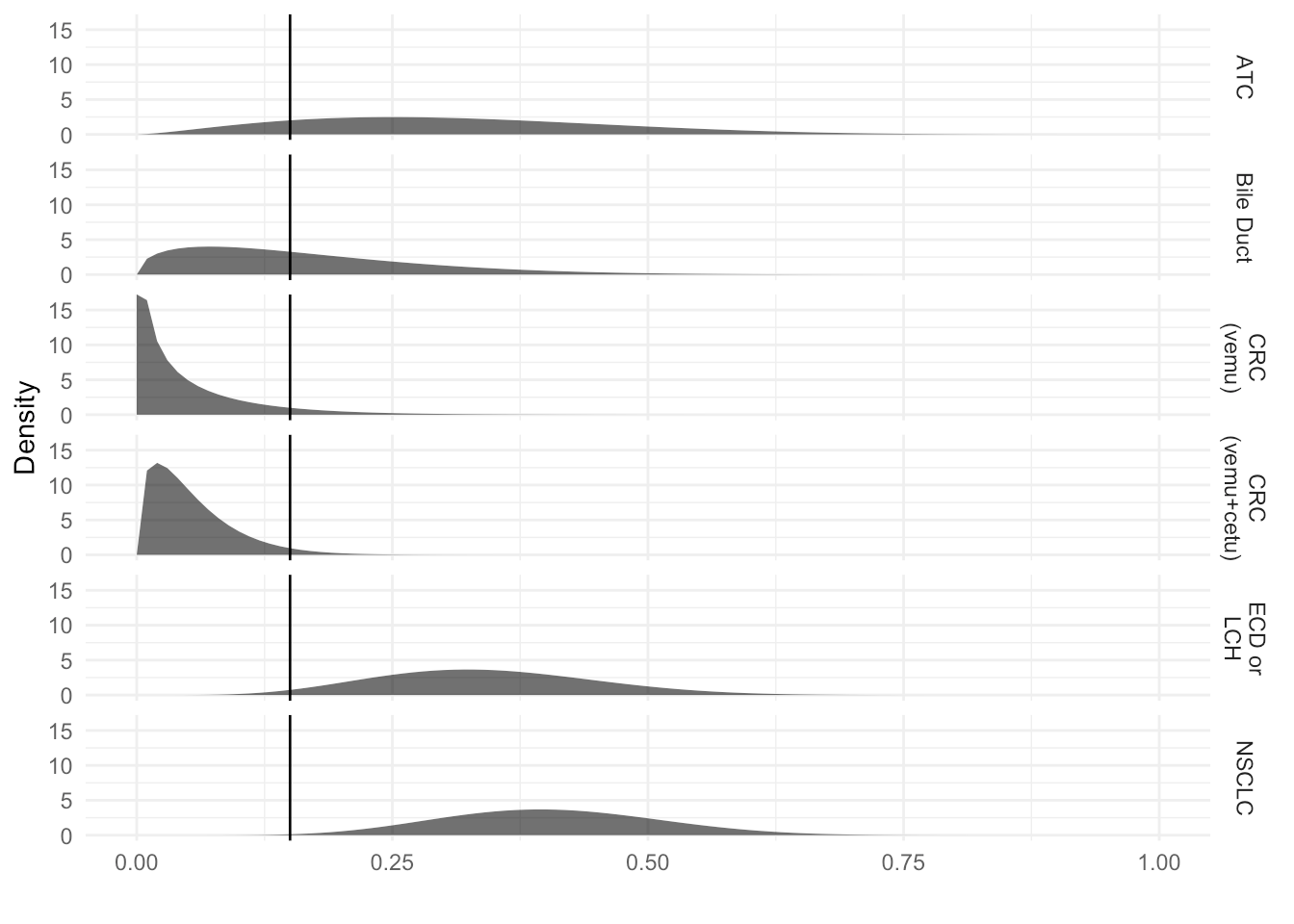
| Indication | Enrolled | Evaluable | Responses | Prob [p > 0.15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCLC | 20 | 19 | 8 | 0.997 |
| CRC (vemu) | 10 | 10 | 0 | 0.06 |
| CRC (vemu+cetu) | 27 | 26 | 1 | 0.03 |
| Bile Duct | 8 | 8 | 1 | 0.47 |
| ECD or LCH | 18 | 14 | 6 | 0.977 |
| ATC | 7 | 7 | 2 | 0.847 |
Individual Arm Distribution
The Multisource Exchageability (MEM) Model Motivation
When the drug works, it is because of a common underlying mechanism of action.
Similar response is driven by the drug.
We should be able to borrow power across similarly responding baskets.
A Bayesian Hierarchical Model is Single-Source
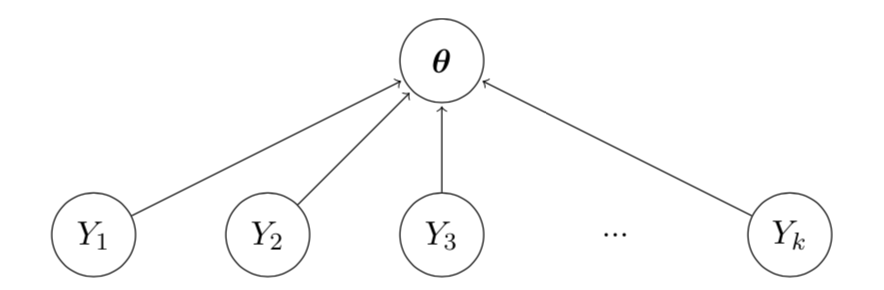
Multiple Sources of Exchangeability
The MEM Model
Finds pair-wise symmetric exchangeability relationships in all possible configurations.
Finds the posterior exchangeability probability (PEP) in all pairs.
Finds the Effective Sample Size (ESS) based on how much power can be borrowed.
Identifies basket clusters using PEP as a measure of similarity.
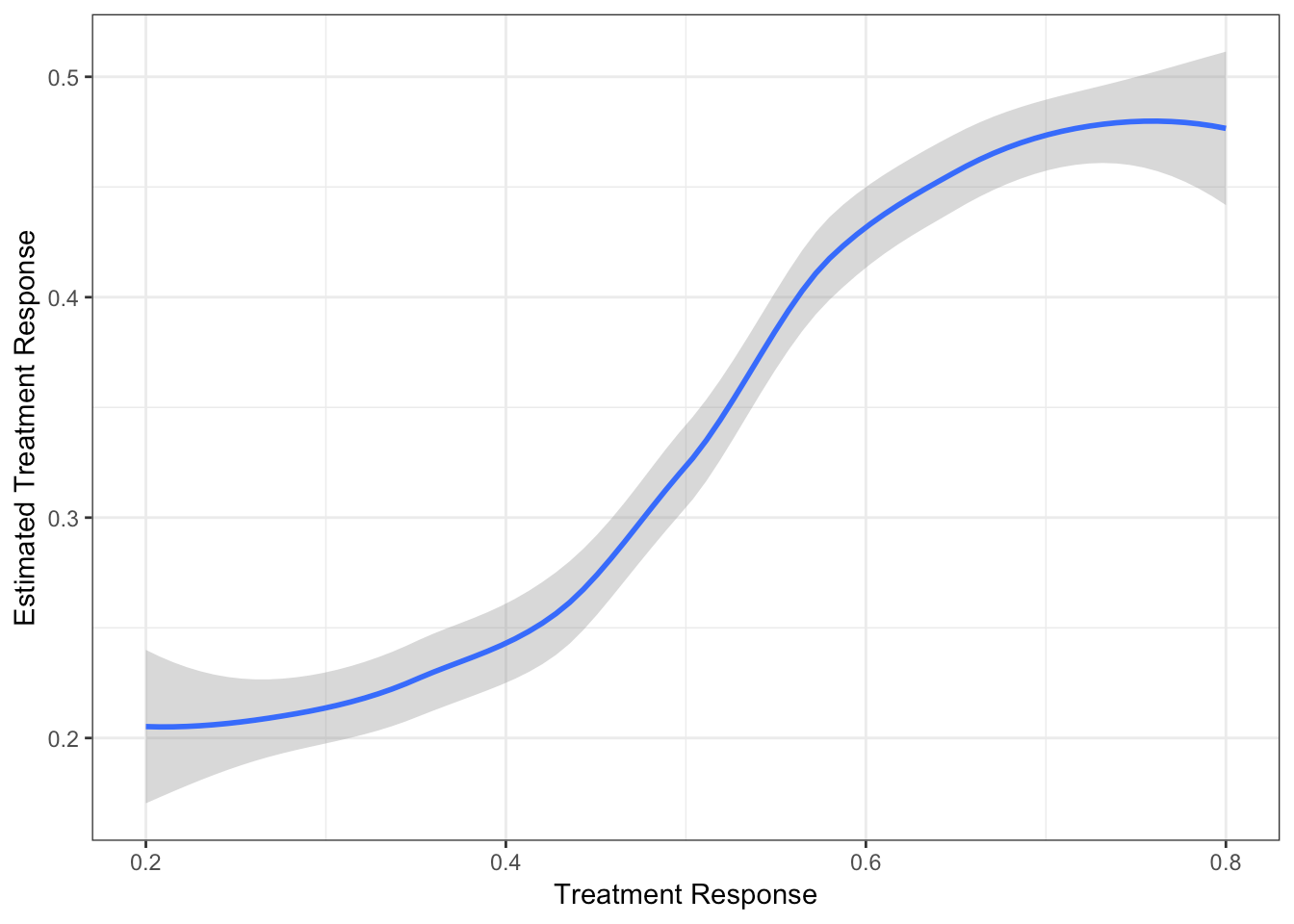
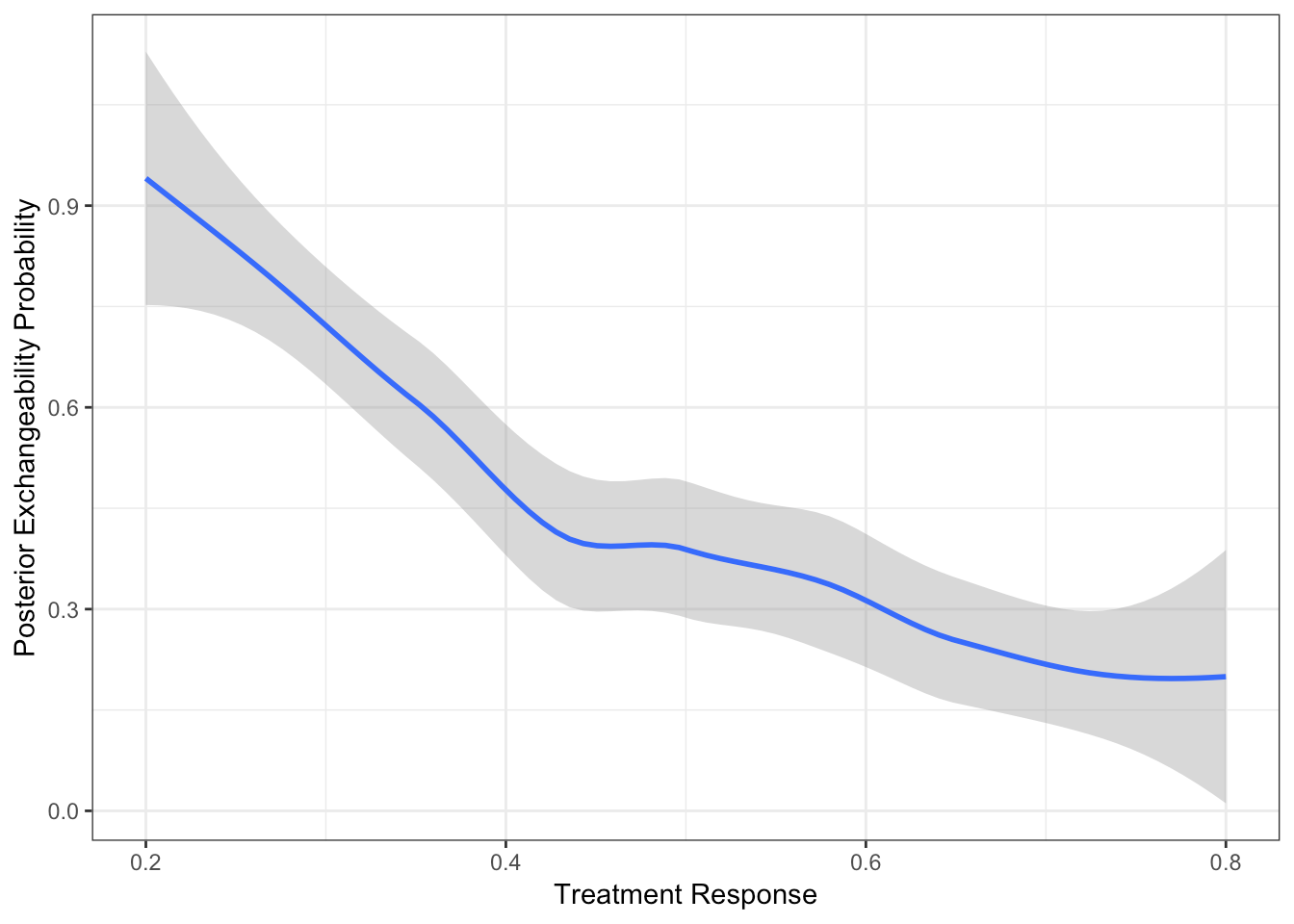
Extent of Borrowing Between Two Baskets
Two baskets each with size 10
Response rate in basket 1 is 0.2
Response rate in basket 2 varies from 0.8 to 0.2
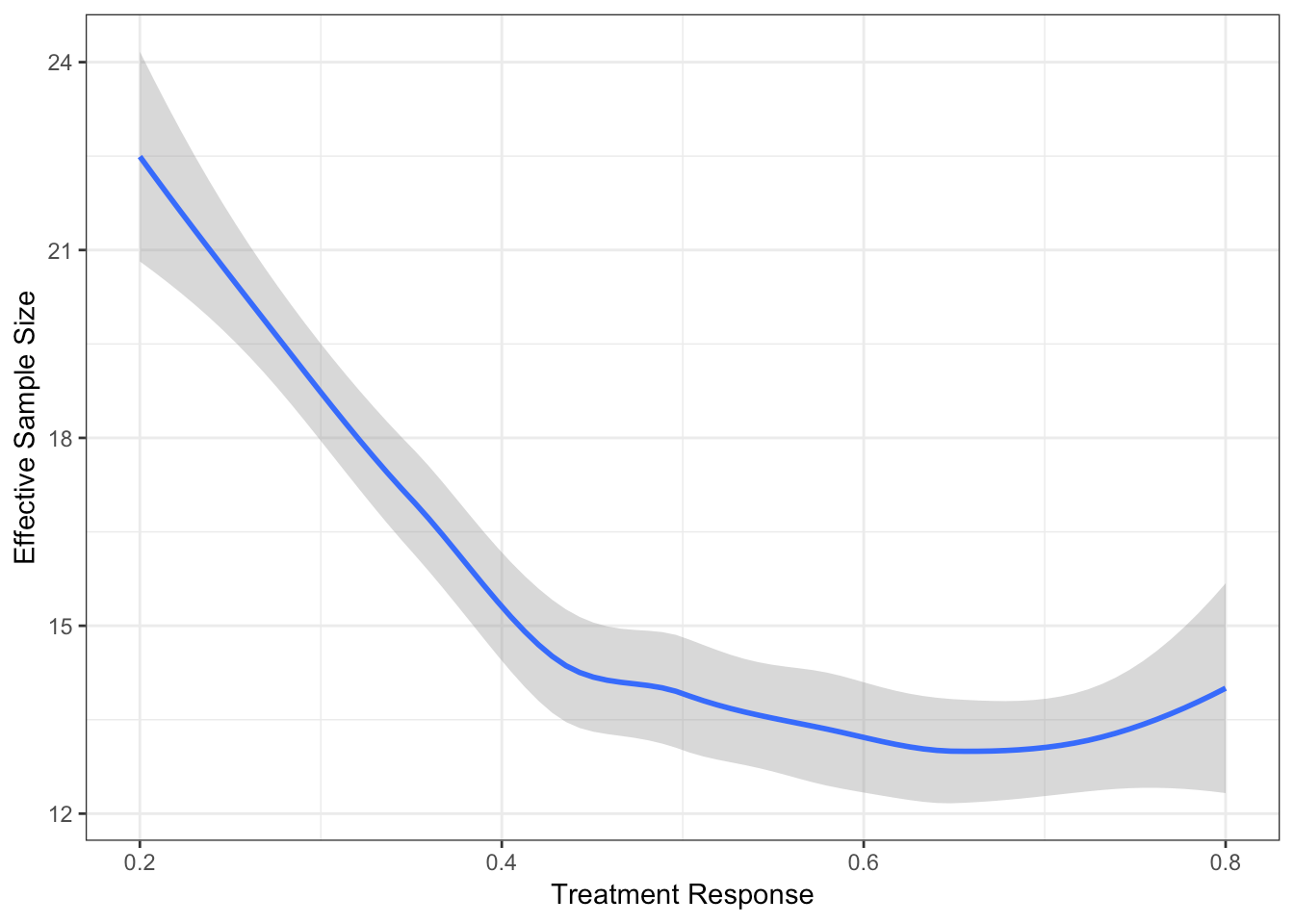
Effective Sample Size of Basket 2
Response Estimate of Basket 2
PEP
Back to Vemurafenib
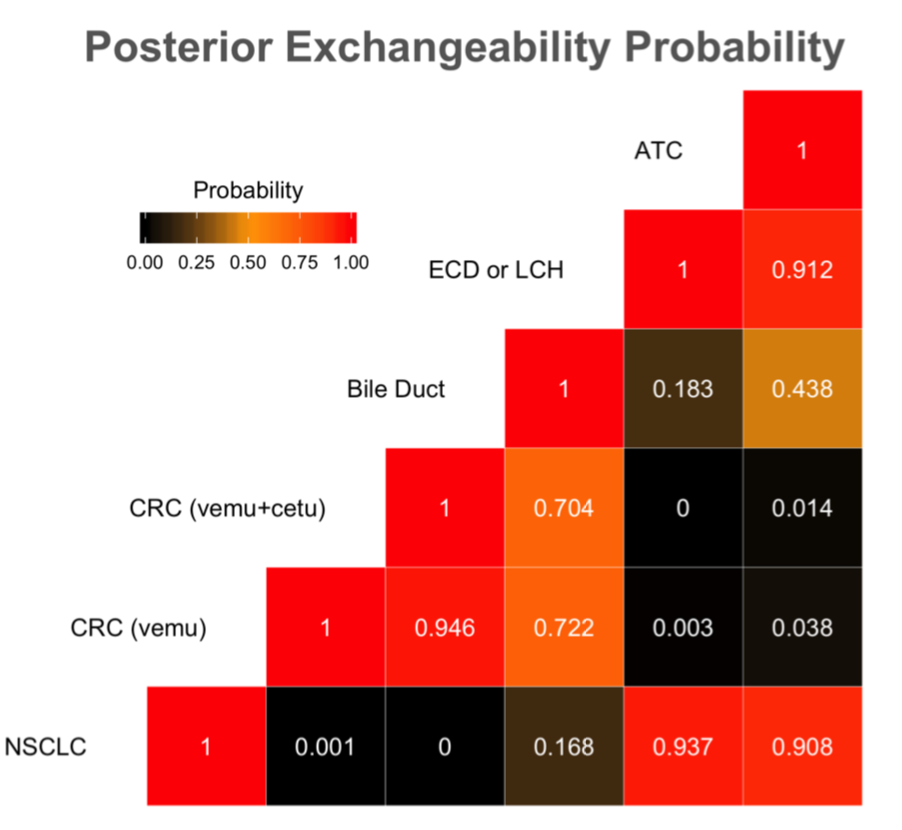
Vemurafenib MEM Analysis
| Indication | Evaluable | ESS | Prob [p > 0.15] | MEM Prob [p > 0.15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCLC | 19 | 38 | 0.997 | 0.999 |
| CRC (vemu) | 10 | 52 | 0.06 | 0.025 |
| CRC (vemu+cetu) | 26 | 56 | 0.03 | 0.017 |
| Bile Duct | 8 | 10 | 0.47 | 0.287 |
| ECD or LCH | 14 | 38 | 0.977 | 0.999 |
| ATC | 7 | 32 | 0.847 | 0.995 |
PEP
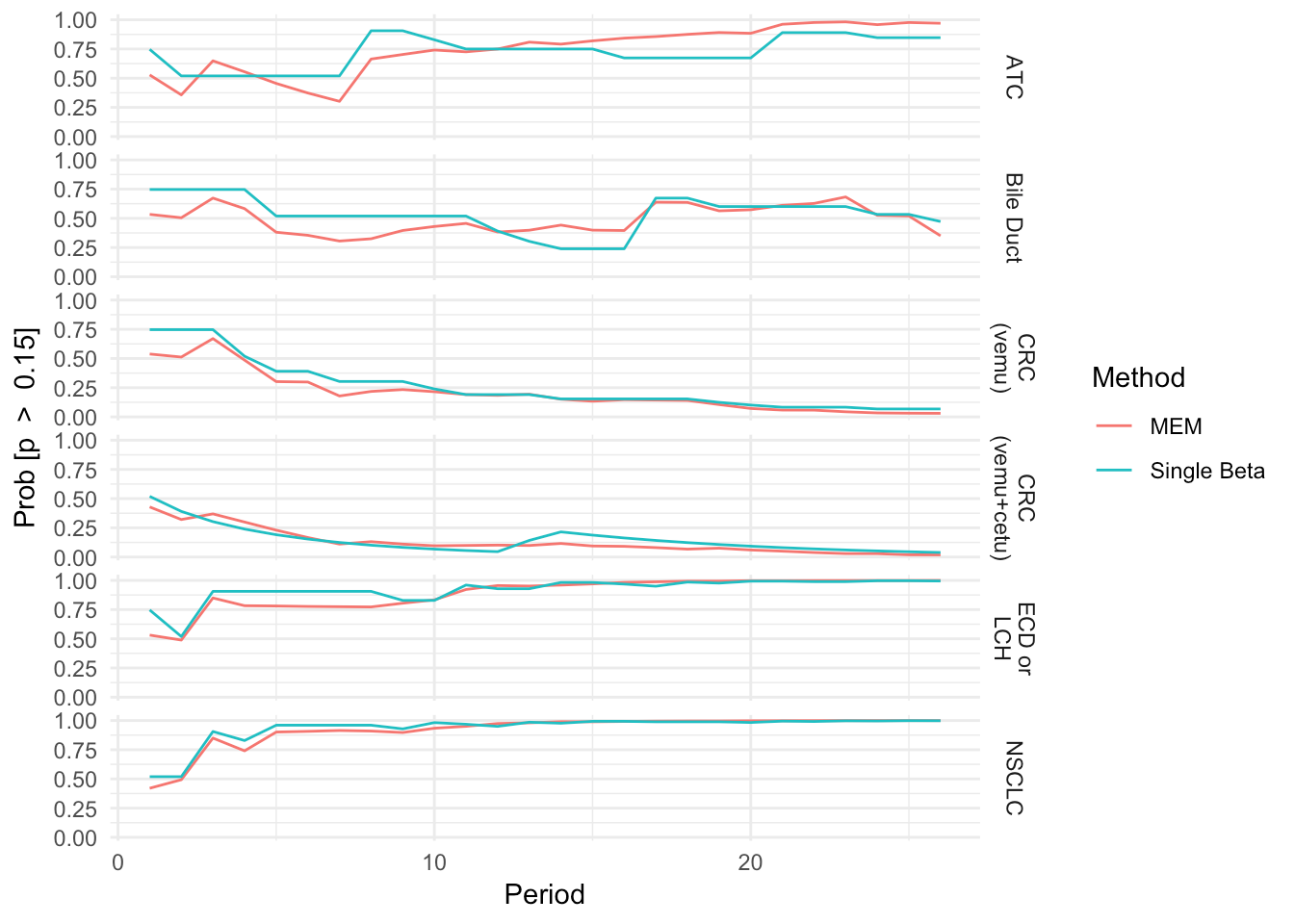
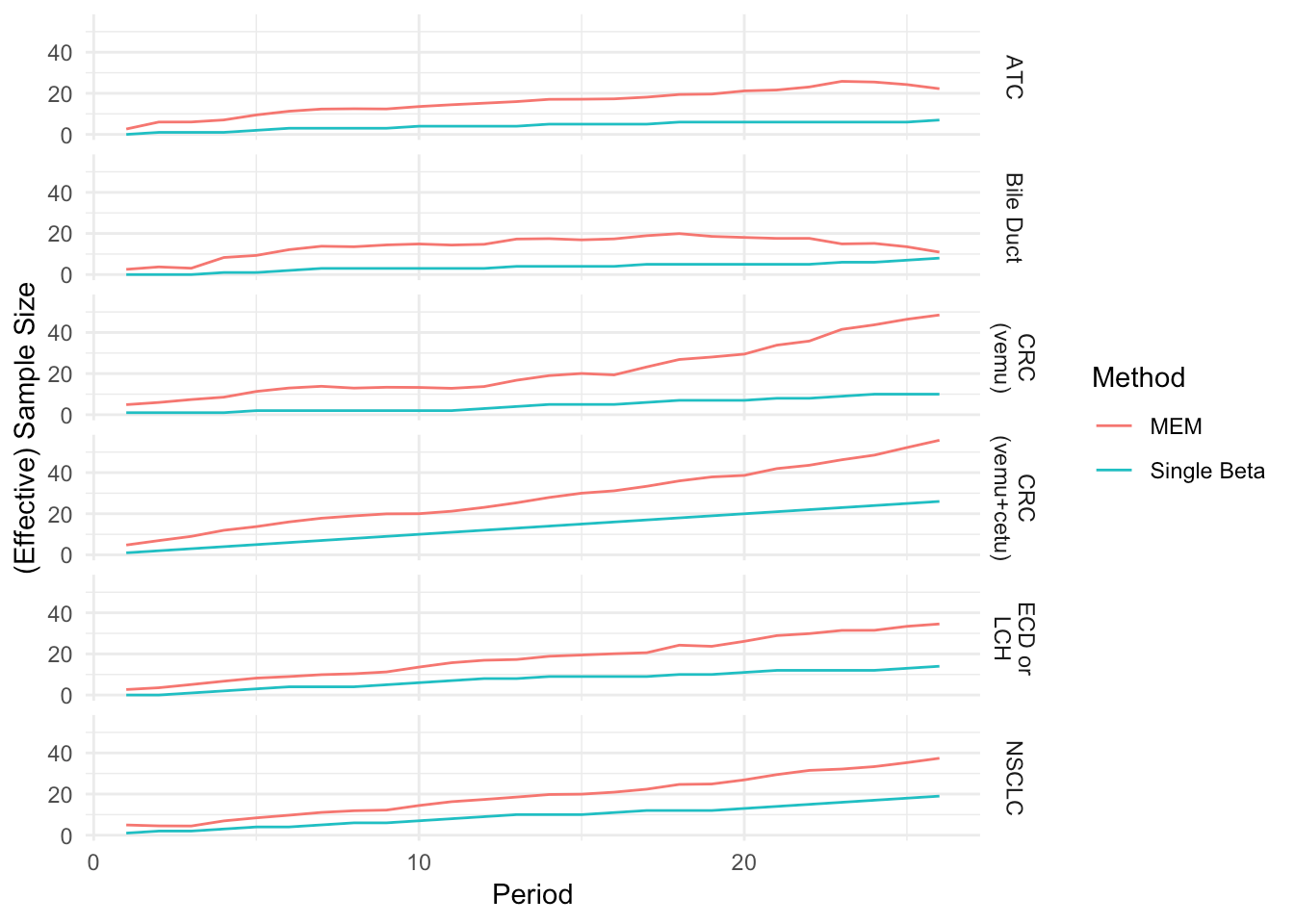
Trial Simulation (1000 Resamples)
Fixed trial duration (26 periods, max number of evaluable patients)
Enrollment times are uniform over the enrollment duration
Responses are uniform over enrollments
Find expected success probability and ESS over time
Expected Arm Success
Sample Size
Going Beyond Basketing by Indication
Vemurfanib Response and Prior Therapy
| Indication | Enrolled | Evaluable | Responses | Prior Therapy <= 1 | Prior Therapy == 2 | Prior Therapy >=3 | MEM Prob [p > 0.15] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NSCLC | 20 | 19 | 8 | 11 (0.55) | 4 (0.2) | 5 (0.25) | 0.999 |
| CRC (vemu) | 10 | 10 | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 2 (0.2) | 7 (0.7) | 0.025 |
| CRC (vemu+cetu) | 27 | 26 | 1 | 5 (0.185) | 11 (0.407) | 11 (0.407) | 0.017 |
| Bile Duct | 8 | 8 | 1 | 2 (0.25) | 1 (0.125) | 5 (0.625) | 0.287 |
| ECD or LCH | 18 | 14 | 6 | 9 (0.5) | 7 (0.389) | 2 (0.111) | 0.999 |
| ATC | 7 | 7 | 2 | 5 (0.714) | 1 (0.143) | 1 (0.142) | 0.995 |
Try a basket trial yourself
install.packages("basket")
vignette("using-the-basket-package")
Thanks
Considerations for Basket Trial Design under Multisource Exchangeability Assumptions
By Michael Kane
Considerations for Basket Trial Design under Multisource Exchangeability Assumptions
ICSA 2019
- 1,451


